Factors Affecting the Cost per Square Foot of Geocells
Factors influencing the cost per square foot of geocells can be broken down into six core dimensions: material properties, product specifications, production process, procurement conditions, performance standards, and market environment. Each dimension is directly or indirectly related to geocell prices and is closely related to actual engineering applications (such as roadbed reinforcement, slope protection, and wetland restoration). Today, Lianxiang Geotechnical will explain the factors affecting the cost per square foot of geocells, combining industry standards and engineering practice details.

1. Core Factors: Material Properties and Modification Requirements
The raw materials and modification treatments of geocells form the basis of cost, directly determining the unit area material cost and performance threshold.
1.1. Substrate Type (Core cost accounts for 30%-50%)
- Mainstream substrates: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP). The cost difference between the two is approximately 10%-20% (HDPE has stronger weather resistance and a slightly higher cost; PP has good rigidity but significant low-temperature brittleness and a lower cost).
- Material Grade: Virgin resin vs. Recycled plastic granules. Virgin resin costs 20%-40% more than recycled resin, but its tensile strength and creep performance meet standards more readily (virgin resin is required to meet ASTM D6474 Class 1 standards; recycled resin is only suitable for temporary projects or low-strength applications).
1.2. Modified Additives (Cost Increase 5%-30%)
- Anti-aging Modification: Adding carbon black (2%-3%) and UV stabilizers for long-term outdoor projects (e.g., roadbeds, slopes) increases cost by 8%-15%; unmodified products are only suitable for indoor or short-term use.
- Special Environment Modification: Acid and alkali resistance (adding corrosion inhibitors), flame retardancy (adding bromine-based or halogen-free flame retardants), low-temperature resistance (adding toughening agents) for chemical plants, high-altitude and cold regions, etc., increases cost by 15%-30%.
- Environmental Requirements: Environmentally friendly additives that comply with EU RoHS and REACH certifications cost 5%-10% more than ordinary additives.
2. Key Variables: Product Specifications and Structural Design
The physical parameters of geocells directly affect the material consumption per unit area and the difficulty of production, and are the main cause of cost fluctuations.
| Specifications | Impact Logic | Cost Fluctuation Range (per square foot) |
| Cell Height (50-300mm) | Higher height requires more sheet material (volume is proportional to height), and welding process becomes more difficult. | 50mm→300mm, cost increases by 100%-150% |
| Sheet Thickness (1.0-3.0mm) | For every 0.5mm increase in thickness, the weight per unit area increases by 50%, and raw material costs rise accordingly (thickness must meet ISO 10318 tensile strength requirements). | 1.0mm→3.0mm, cost increases by 200%-250% |
| Aperture Size (200-600mm) | Smaller aperture results in higher weld point density (reduced production efficiency), but slightly less material usage; excessively large apertures may require thicker sheet material to compensate for strength. | 200mm → 600mm, cost reduction of 10%-15% (requires matching sheet thickness) |
| Welding strength (≥2.5kN/m) | Ultrasonic welding vs. hot melt welding: Ultrasonic welding (high degree of automation, stable strength) costs 5%-10% more than hot melt welding; the smaller the weld point spacing (e.g., 100mm vs. 200mm), the cost increases by 15%-20% | - |
| Weight per unit area (200-800g/㎡) | Weight is directly related to sheet thickness and aperture, and is a core indicator for cost accounting (cost increases by 10%-12% for every 100g/㎡ increase) | 200g/㎡ → 800g/㎡, cost increase of 300%-350% |
| Structural type (standard vs. reinforced) | Reinforced type (thickened edges, cross-rib reinforcement) is used in high-load scenarios (e.g., heavy-duty roadbeds), increasing material usage by 20%-30% | Cost Increase of 25%-40% |
3. Impact on Production: Technological Level and Economies of Scale
Efficiency, equipment investment, and quality control in the production process are directly amortized into unit area costs. Large-scale production can significantly reduce marginal costs.
3.1. Production Equipment and Automation Level
- Imported Equipment (e.g., Coperlon (Germany), Lesso (China): Automated welding, continuous molding, low scrap rate (≤3%), unit cost 10%-15% lower than domestic manual equipment, but high depreciation costs (large initial investment).
- Domestic Equipment: Semi-automatic production lines have a higher scrap rate (5%-8%), and labor costs account for a higher proportion (approximately 15%-20%), suitable for small-batch orders.
3.2. Production Scale and Order Volume
- Bulk Orders (≥10,000㎡): Suppliers can reduce costs through centralized raw material procurement and optimized production scheduling, with a discount of approximately 10%-20% per unit area.
- Small Batch Orders (≤1,000㎡): Requires separate mold debugging and production arrangement. After amortizing the mold cost (approximately 5,000-10,000 RMB/set), the unit cost increases by 25%-40%.
3.3. Scrap Rate and Production Efficiency
- Standard production scrap rate ≤5%. If the scrap rate rises above 10% due to complex specifications (such as irregular hole diameters or special dimensions), the unit cost increases by 8%-12%.
- Automated production line efficiency (1000-2000㎡/day) is 4-5 times that of manual lines (200-500㎡/day), reducing labor costs by 30%-40%.
4. Procurement-Side Variables: Order Terms and Additional Costs
The transportation, customization, and service requirements in the procurement process directly affect the price of geocells per unit area, especially for large-volume products.
4.1. Order Quantity and Delivery Terms
- Transportation Costs: Geocells still have a relatively large volume after folding (approximately 0.01-0.02 m³ per square meter). For every additional 1000 kilometers of transportation distance, the unit area transportation cost increases by $0.05-0.1 per square foot (sea freight is 30%-40% cheaper than land freight, suitable for international procurement).
- Payment and Delivery Time: A prepayment ratio of ≥50% can reduce the supplier's capital costs, resulting in a 3%-5% discount on unit costs; expedited delivery (≤7 days) requires overtime fees, increasing costs by 10%-15%.
4.2. Customization Requirements
- Size Customization: Non-standard sizes (such as unconventional heights or apertures) require redesigned molds, with mold costs allocated to the product, increasing the unit area by $0.1-0.3 per square foot.
- Labeling and Packaging: Adding project labeling, English instructions (for export orders), or using moisture-proof packaging (for humid environments) increases costs by 2%-5%.
4.3. Additional Services
- Technical Support: Supplier-provided on-site installation guidance and construction plan optimization increase service costs by 3%-8%.
- Quality Inspection: Third-party testing (e.g., SGS, CTI) report fees, after allocation, increase unit area costs by $0.03-0.08/square foot (mandatory for large projects).
5. Quality and Standards: Performance Thresholds and Certification Costs
Products meeting higher standards or certifications have significantly higher unit area costs due to stricter quality control and higher testing costs.
5.1. Industry Standards and Performance Indicators
- Basic Standards: Compliant with GB/T 19274 (China), ASTM D6474 (USA), and ISO 10318 (International), requiring tensile strength ≥10kN/m and creep rupture time ≥1000h, increasing costs by 10%-15% compared to non-standard products.
- High-level standards: For applications such as airport runways and high-speed railways, tensile strength ≥20kN/m and weather resistance ≥5000h (xenon lamp aging test) are required, increasing costs by 30%-50%.
5.2. Certification and Compliance Costs
- International Certifications: CE (EU), ASTM (USA), TÜV (Germany) certifications, with a single certification costing approximately US$10,000-50,000, increasing costs by US$0.05-0.1 per square foot (certification validity 1-3 years).
- Environmental and Safety Certifications: Compliance with US LEED and EU EPD (Environmental Product Declaration) increases costs by 8%-12% (preferred for green building projects).
6. Market Environment: Supply and Demand and Raw Material Fluctuations
Macroeconomic market factors indirectly affect geocell prices by influencing raw material prices and industry competition.
6.1. Raw Material Price Fluctuations
- HDPE and PP prices are strongly correlated with crude oil prices. A $10/barrel fluctuation in crude oil prices leads to a 5%-8% fluctuation in plastic granule prices, which is then passed on to geocells, causing a 3%-6% fluctuation in unit area cost (e.g., a 20% increase in crude oil prices in 2023 would result in an average 8%-12% increase in geocell costs).
6.2. Industry Supply and Demand
- Peak demand seasons (spring and autumn construction peaks): Tight supply and demand, with suppliers offering 5%-10% premiums.
- Overcapacity (e.g., expansion by small and medium-sized manufacturers): Intense price competition, potentially reducing unit costs by 5%-10% (but caution is advised regarding recycled materials and low-standard products).
6.3. Regional Cost Differences
- Production Regions: China (Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta) has lower labor and energy costs, resulting in unit area costs that are 30%-50% lower than those produced in Europe and America (70% of global geocells are produced in China).
- Taxes and Tariffs: Cross-border procurement incurs tariffs (e.g., the US tariff on Chinese geosynthetic materials is approximately 10%-25%), increasing unit costs by 10%-25%.
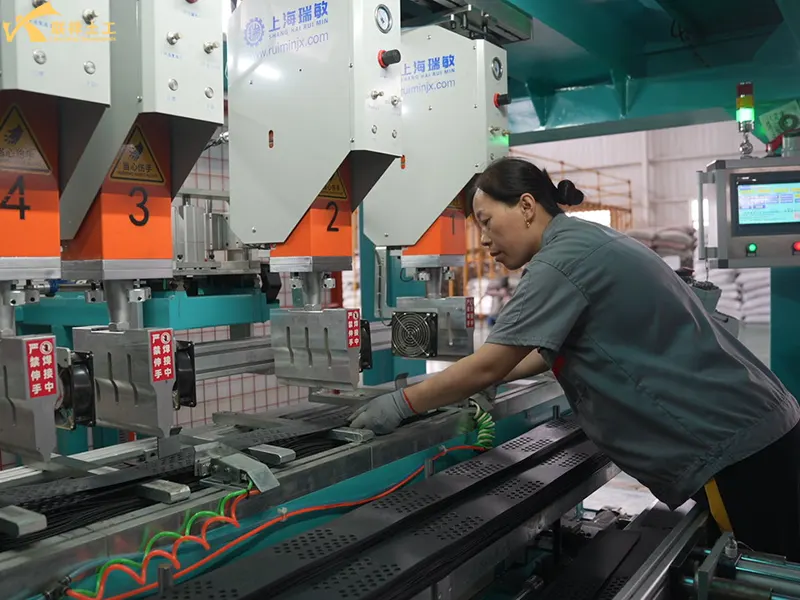
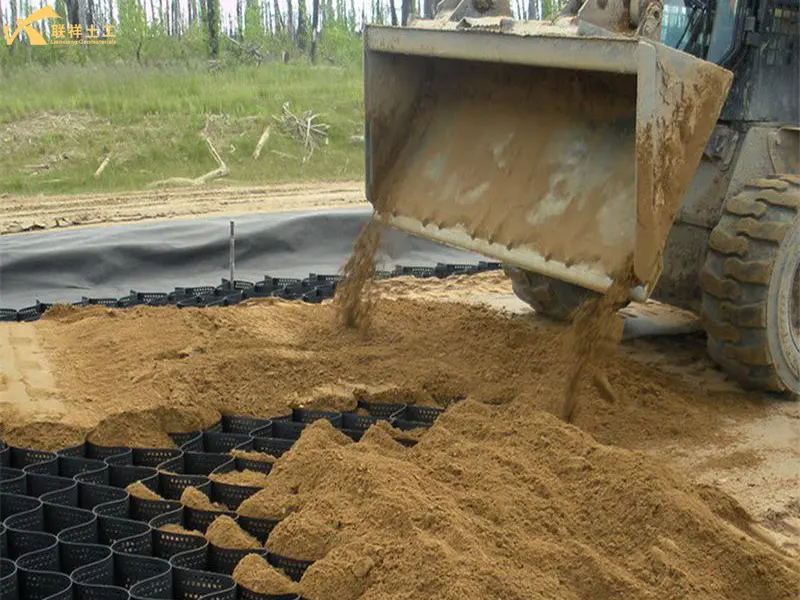


7. Cost Optimization Recommendations (Based on Project Specifics)
7.1. Specification Selection: Match the scenario, avoid over-design
- Ordinary roadbed reinforcement: Choose HDPE material, height 100-150mm, thickness 1.5-2.0mm (meeting foundation standards). High thickness or special modifications are unnecessary, reducing costs by 20%-30%.
- Short-term temporary projects (e.g., temporary access roads): Recycled materials + foundation modification products can be used, reducing costs by 30%-40% (but the service life must be specified as ≤2 years).
7.2. Procurement Strategy: Scale and Local Procurement
- Jointly procure in bulk for multiple projects (≥20,000㎡) to secure the maximum supplier discount (15%-20%).
- Prioritize local or surrounding suppliers to reduce transportation costs (e.g., procuring from East China, transportation costs are 40%-60% lower than from Northwest China).
7.3. Quality and Cost Balance: Rejecting "Low Standard, Low Price"
- Non-standard products (recycled materials + unmodified) have 30% lower initial costs, but their lifespan is only 1/3-1/2 that of standard products, resulting in higher long-term maintenance costs (e.g., in slope protection projects, low-standard products need to be replaced every 3-5 years, while standard products can be used for 15-20 years).
8. Conclusion
The core drivers of the cost per square foot of geocells are raw material quality + product specifications + production scale (these three account for 70%-80% of the total cost), followed by additional costs such as transportation, certification, and customization. In engineering practice, cost and performance are positively correlated. It's crucial to select appropriate products based on the project's service life, load conditions, and environmental requirements, avoiding either "blindly pursuing low prices" or "over-design." For accurate cost estimation, the following parameters are required: cell height/thickness/pore size, raw material type (virgin/recycled), modification requirements (anti-aging/acid/alkali resistance, etc.), order quantity, delivery location, and standard requirements. Suppliers can use this information to provide accurate geocell pricing. Lianxiang Geotechnical has been engaged in the production, R&D, and sales of geocells for many years. The company can design products best suited to the specific needs of clients, satisfying their requirements while saving them costs. Please contact us for consultation.
Written by
SHANDONG LIANXIANG ENGINEERING MATERIALS CO., LTD.
Kyle Fan
WhatsApp:+86 139 5480 7766
Email:admin@lianxiangcn.com
Contact
-
WhatsApp
-
E-MailE-Mail:admin@lianxiangcn.com
-
WeChatWeChat:18554180188









