- Description
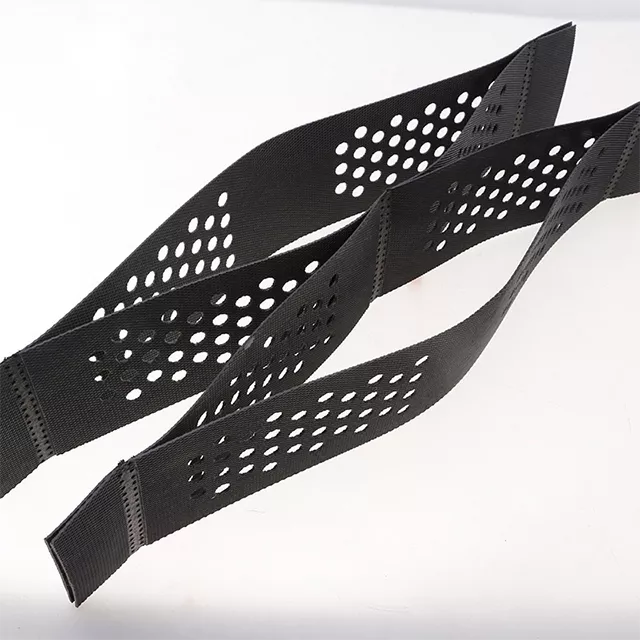
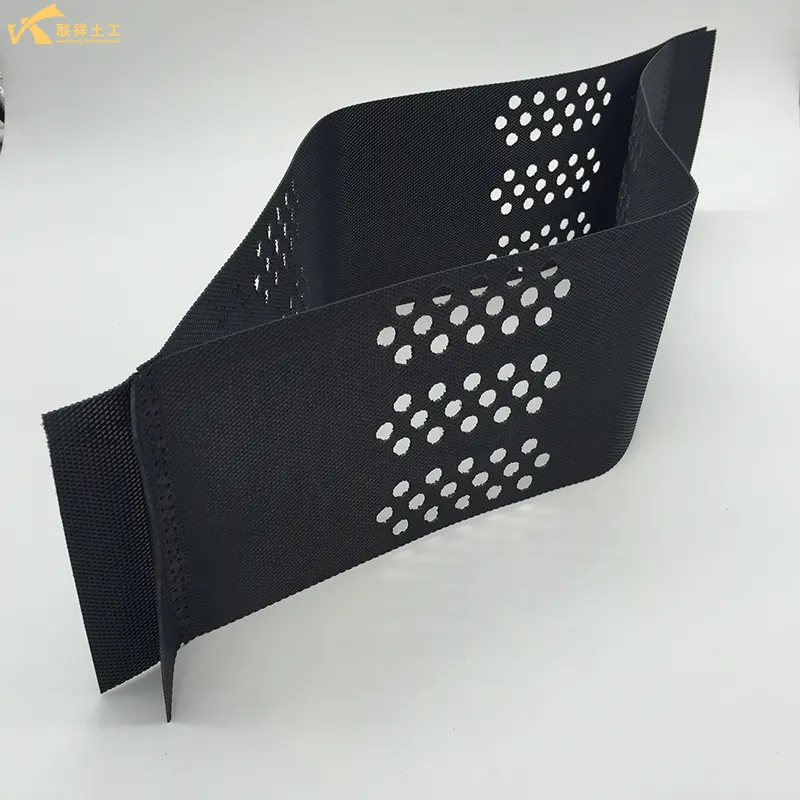
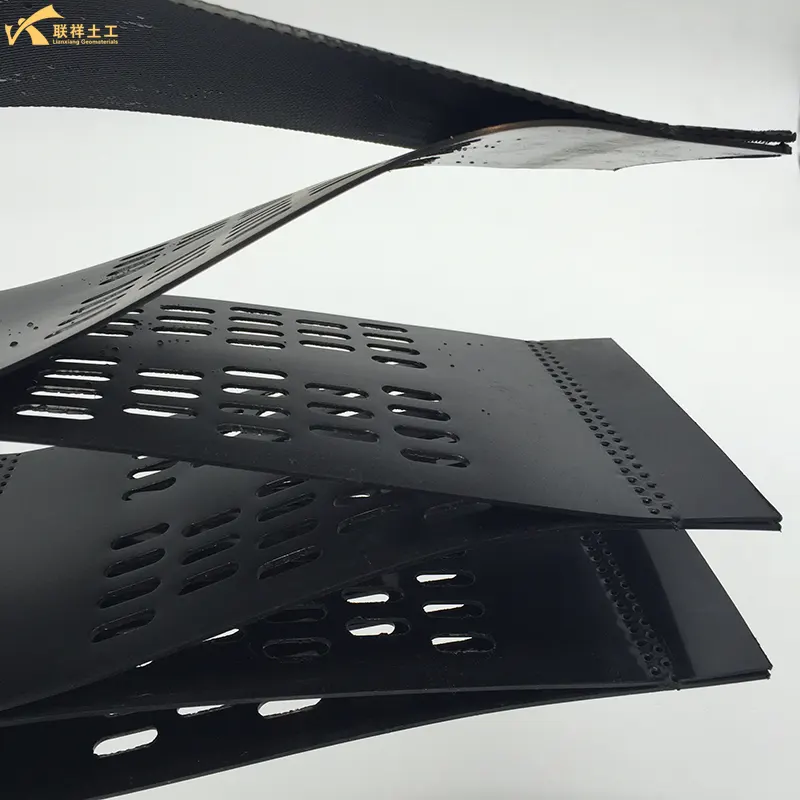
Geocell is a three-dimensional mesh structure made of long plastic strips ultrasonically welded together. When unfolded, it forms a three-dimensional grid. Perforations can sometimes be added to meet customer needs. The height, weld spacing, and sheet thickness of the geocell significantly impact its engineering performance. In engineering applications, different geocell types can create cushions with varying degrees of adhesion, reinforcement strength, and thickness.



Introduction
Geocells are perforated or not, depending on customer needs. Perforations enhance their ecological function and drainage performance. Geocell height, weld spacing, and sheet thickness significantly impact their engineering performance. In engineering, different geocell types can form cushions with varying degrees of adhesion, reinforcement strength, and thickness. These cushions can be positioned as needed for road and railway subgrade reinforcement, slope protection, and retaining wall construction. The width of the strip is the height of the geocell. When the sheet is not unfolded, the distance between two welds on the same side is the weld distance.
Features:
- 1. Three-Dimensional Structure: Unlike two-dimensional geogrids or geotextiles, geocells provide three-dimensional restraint, enabling more effective load distribution.
- 2. Lateral Confinement: The cellular structure securely locks the fill material within the cells, preventing lateral movement and loss.
- 3. Stress Diffusion: It distributes concentrated surface loads (such as vehicle wheel pressure) more evenly across a wider area of the base soil, reducing the pressure on the foundation.
- 4. Flexible System: It offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, adapts to uneven foundation settlement, and is less susceptible to fracture.
Main Materials:
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE): The most commonly used material, offering excellent chemical resistance, aging resistance, and durability.
- Polypropylene (PP): High strength, but slightly less durable than HDPE under UV rays. It is often used in short-term projects or under cover layers.
Main Parameters:
- Cell Height (H): Common cell heights include 50mm, 75mm, 100mm, 150mm, 200mm, and 300mm. The height determines the thickness and bearing capacity of the reinforcement layer.
- Welding Spacing: The size of a single cell. Common sizes include 330x330mm, 400x400mm, and 500x500mm. The smaller the weld spacing, the higher the density and the stronger the restraint.
- Sheet Thickness (d): Typically, it ranges from 1.0mm, 1.1mm, to 1.5mm. Thickness affects the overall strength and durability of the cell.
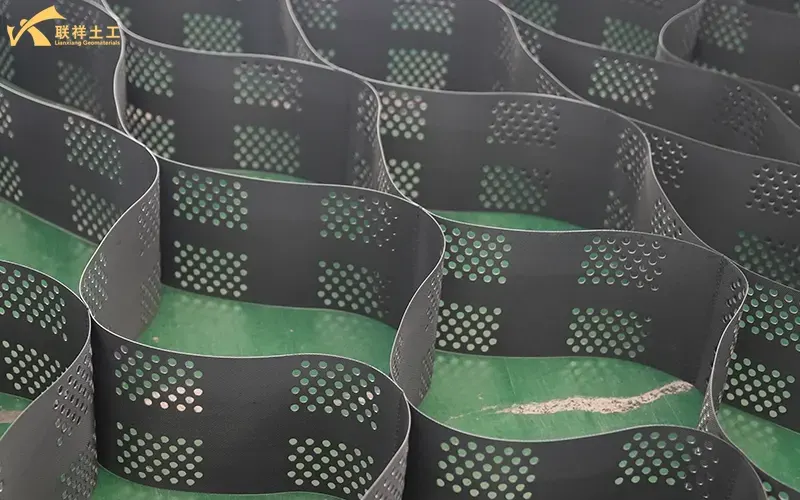



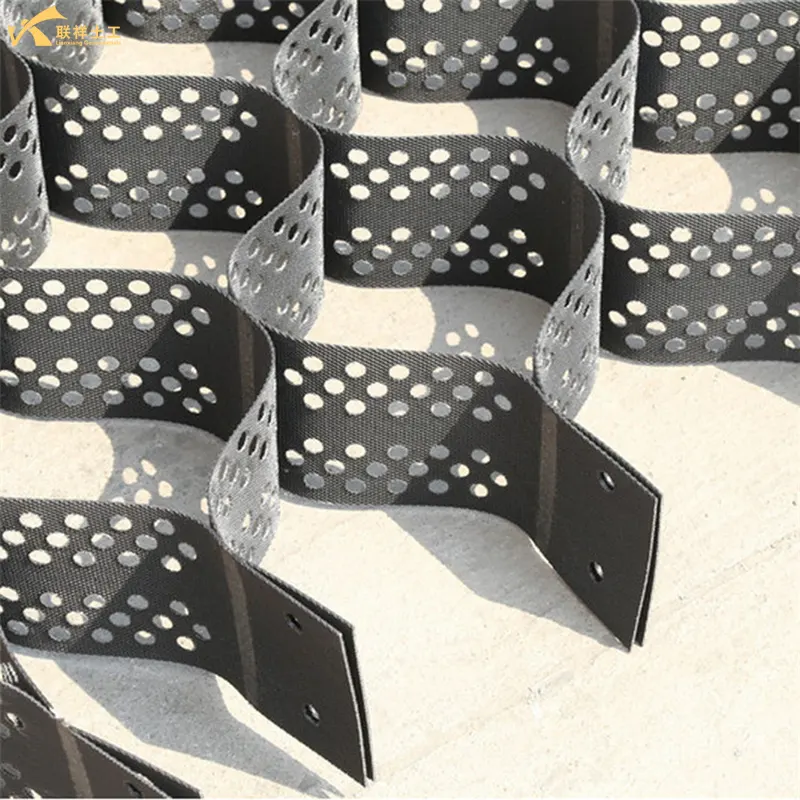
Core Working Principle
The core working principles of geocells can be summarized as "three-dimensional reinforcement and restraint" and the "high-stiffness platform effect."
- 1. Three-Dimensional Constraint Mechanism: When the cells are expanded and filled, their side walls exert strong friction and circumferential restraint on the loose filler inside, preventing lateral displacement and vertical deformation under load. This enables the formation of a structural layer with high strength and stiffness, even with inexpensive local fillers (such as sand and gravel).
- 2. Uniform Load Distribution: When loads act on the cell layers, their three-dimensional network structure partially converts vertical stresses into horizontal stresses. Like an elastic raft, it redistributes the stresses over a larger area, significantly reducing the actual compressive stress on the underlying soft foundation and preventing destructive deformation.
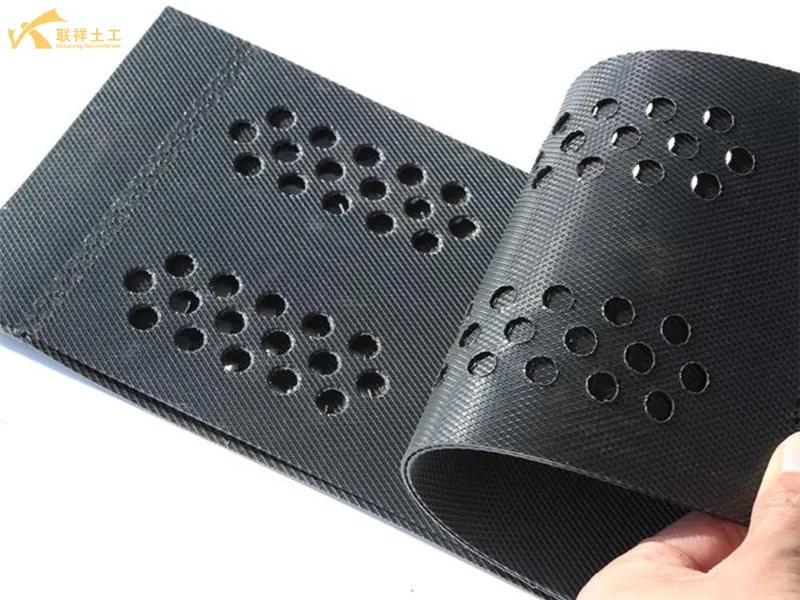

Main Application Areas
Geocells are extremely versatile and can be found in virtually all engineering applications requiring soft foundation treatment, slope stability, and load distribution.
1. Highway and Railway Engineering
- Soft Foundation Treatment: Used for roadbed reinforcement in highways and railways, particularly in soft soils, swamps, backfill, and other areas with insufficient bearing capacity. It effectively reduces differential settlement and prevents pavement cracking.
- Roadbed Widening: Used at the junction of new and old roadbeds, it can reduce differential settlement and prevent longitudinal cracking.
- Slope Protection: Used on embankment slopes to prevent rainwater erosion and soil loss. Temporary Roads/Access Roads: In areas where temporary heavy-duty roads need to be quickly constructed, such as construction sites, oil fields, and wind farms, geocells can quickly form a stable platform to allow heavy equipment to pass.
2. Water Conservancy Projects
- River and Canal Slope Protection: Prevents water from eroding bank slopes, maintaining bank stability while allowing vegetation to grow, creating an eco-friendly environment.
- Reservoir/Dam Slope Protection: Protects the dam from wind and wave erosion and rainwater erosion.
- Hydraulic Structure Foundation Reinforcement: Used to treat soft foundations beneath structures such as sluice gates and pumping stations.
3. Civil and Geotechnical Engineering
- Retaining Wall/Abutment Backfill Reinforcement: Combined with the facing wall, this reinforced earth retaining wall reduces lateral earth pressure and improves stability.
- Pipeline/Culvert Support: Distributes the pressure from upper backfill and ground loads on pipelines, preventing deformation or rupture.
- Landfill Pad: Used in the base and cover layers to improve overall stability.
4. Military Engineering
- Rapid Construction of Temporary Runways and Landing Sites: Its lightweight and rapid deployment makes it ideal for military applications, creating platforms suitable for heavy equipment on harsh terrain in a very short time.
5. Ecological and Environmental Engineering
- Ecological Slopes: Filling the cells with soil and planting soil provides a stable base for plant growth, achieving a perfect combination of engineering protection and ecological greening.
- Desert and Beach Road Construction: In areas lacking stable materials, filling the cells with local sand and soil creates a stable roadbed.
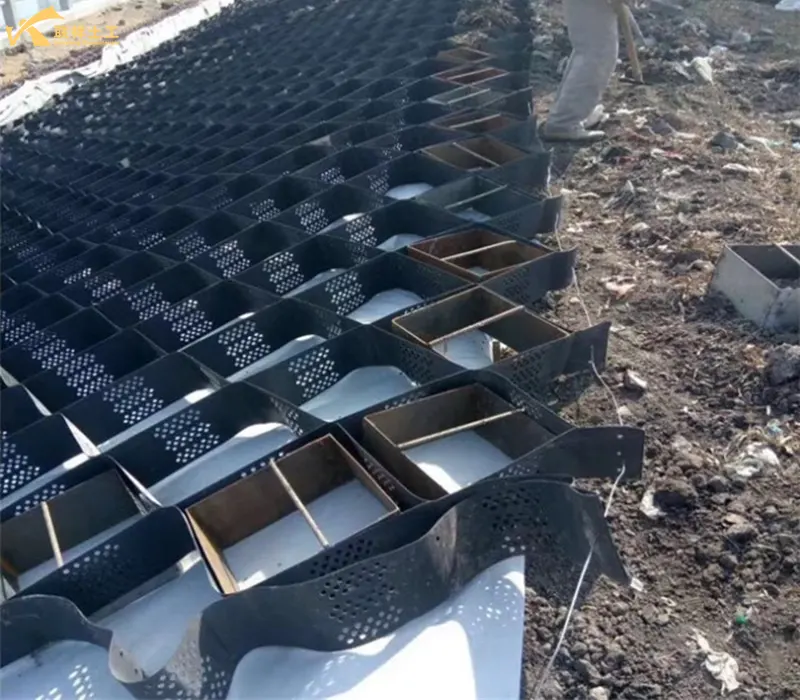
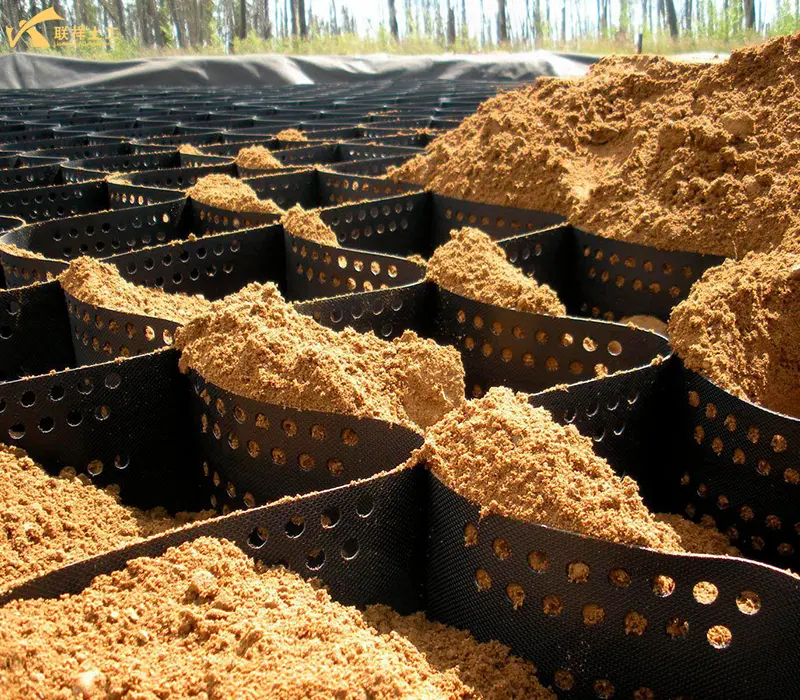
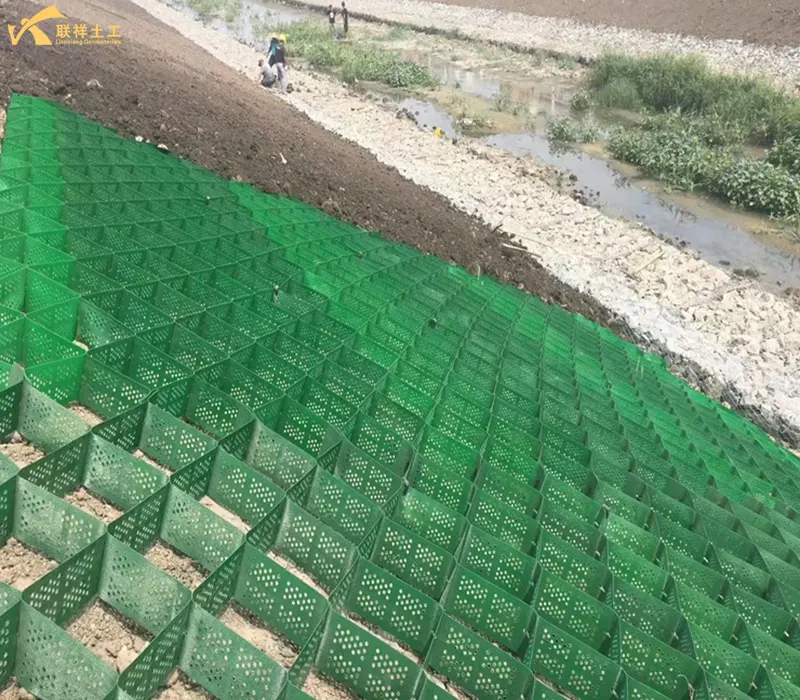



Brief Construction Steps
- 1. Foundation Preparation: Level the site to create the desired slope or flat surface.
- 2. Laying the Cells: Unfold and level the folded cells, ensuring they are fully extended. Use anchors or U-shaped nails to secure them to the foundation to prevent shifting.
- 3. Filling Material: Use a suitable filler (sand, stone, gravel, soil, etc.) to fill the cells from the edges toward the center. The fill can be dumped using an excavator, loader, or dump truck, then leveled with a scraper and finally compacted with a vibrating plate.
- 4. Compaction: Compact during or after filling to ensure the fill is dense.
- 5. Cover Layer Construction: Lay the next structural layer (such as a base layer or surface layer) or apply landscaping on the already filled and compacted geocell layer.
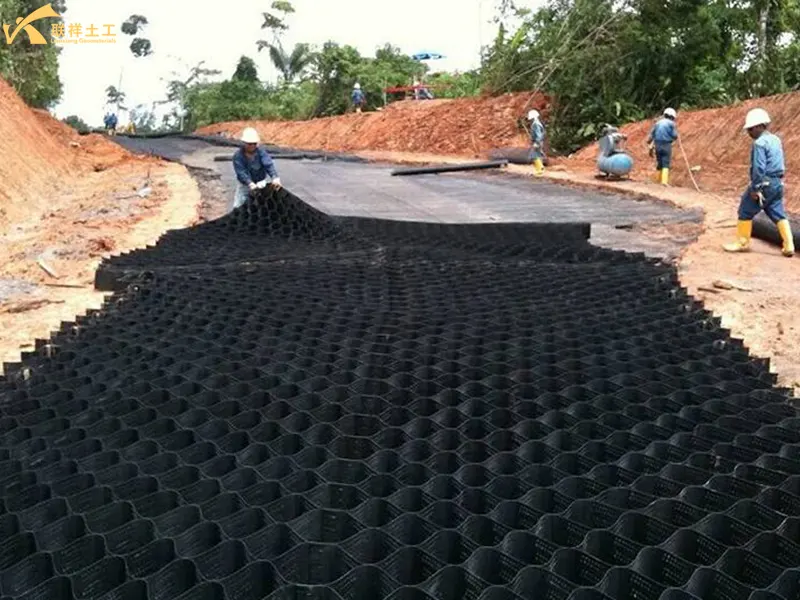

Specification
| Item Model | Height/mm | Welding distance /mm |
Strip thickness(mm) | Expanded Cell Size/mm | Expanded panel size/m |
|
| smooth | textured | |||||
| TGLG-100-330 | 100 | 330 | 1.0-1.2 | 1.3-1.7 | 244X203 | 2.44X6.15 |
| TGLG-150-330 | 150 | 244X203 | 2.44X6.15 | |||
| TGLG-200-330 | 200 | 244X203 | 2.44X6.15 | |||
| TGLG-100-356 | 100 | 356 | 1.0-1.2 | 1.3-1.7 | 259X224 | 2.56X6.52 |
| TGLG-150-356 | 150 | 259X224 | 2.56X6.52 | |||
| TGLG-200-356 | 200 | 259X224 | 2.56X6.52 | |||
| TGLG-100-400 | 100 | 400 | 1.0-1.2 | 1.3-1.7 | 295X250 | 4X5 |
| TGLG-150-400 | 150 | 295X250 | 4X5 | |||
| TGLG-200-400 | 200 | 295X250 | 4X5 | |||
| TGLG-100-445 | 100 | 445 | 1.0-1.2 | 1.3-1.7 | 320X287 | 2.56X8.35 |
| TGLG-150-445 | 150 | 320X287 | 2.56X8.35 | |||
| TGLG-200-445 | 200 | 320X287 | 2.56X8.35 | |||
| TGLG-100-660 | 100 | 660 | 1.0-1.2 | 1.3-1.7 | 488X406 | 2.44X12.29 |
| TGLG-150-660 | 150 | 488X406 | 2.44X12.29 | |||
| TGLG-200-660 | 200 | 488X406 | 2.44X12.29 | |||



Advantages Summary
- Effectively Improves Bearing Capacity: Significantly improves the bearing capacity of weak foundations.
- Cost Savings: Allows the use of local, inexpensive fill, reducing the cost and environmental impact of purchasing high-quality materials from distant locations.
- Simple and Quick Construction: Manual laying and mechanized filling ensure high construction efficiency.
- Durability: The polymer material is corrosion-resistant and aging-resistant, with a long service life.
- Environmentally Friendly: Can be combined with vegetation to achieve harmony between the engineering structure and the ecological environment.
In summary, geocell is a highly efficient, economical and multifunctional modern geosynthetic material. Through its unique three-dimensional structure, it solves many geotechnical engineering problems that traditional two-dimensional materials are difficult to cope with, and is known as the "king of three-dimensional soil reinforcement."
Contact
-
WhatsApp
-
E-MailE-Mail:admin@lianxiangcn.com
-
WeChatWeChat:18554180188













